Mini-Challenge #2
-
in the spirit of the other mini-challenge i posted:
http://sketchucation.com/forums/viewtopic.php?f=15%26amp;t=44972
this one is a little different (i think) since it's not trying to find a workaround to lack of arcs in sketchup (which has since been made possible with native sketchup tools)
in this one, find a way to place a rectangle inside an odd shaped polygon.. (think of it as a 2x4, with 90º end cuts, crossing an odd shaped room)
here's an example file showing two solved problems as well as includes an unsolved shape.
mc2_example.skp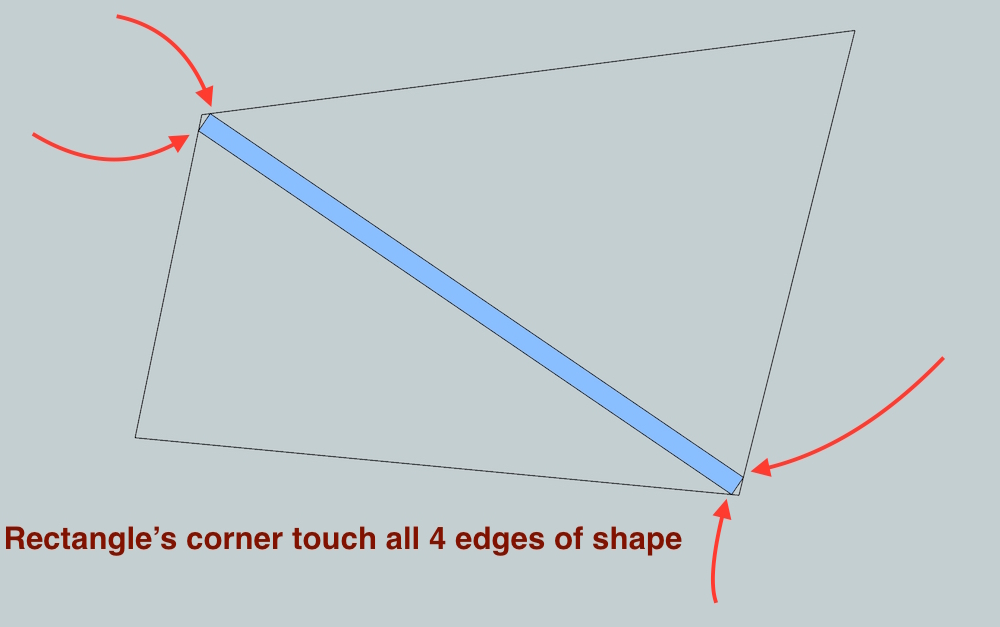
looking for a 'geometric trick' to solve if possible.. i don't know the solution yet.
good luck[EDIT]- the length (or width even) of the rectangle can be any length.. all that's important are that it's a rectangle (all 4 corners 90º)
-
You can use the width and the corner angles to work out the other sides of the two triangles. Technically you only need to solve one other side. The maths involved is beyond my whiskey sozzled brain.
-
@box said:
You can use the width and the corner angles to work out the other sides of the two triangles. Technically you only need to solve one other side. The maths involved is beyond my whiskey sozzled brain.
sober up a bit and try to explain a little better
 (I kid, I kid)
(I kid, I kid)
I'm not sure which width and corner angle you're talking about? -
Actually the whiskey is from years past.
I think, to use your 2x4 analogy, you have a fixed width 2" you have two known angles, the two corners you want to fit between. There must be a formula to work out the lengths of the other two sides of the two triangles formed at the ends given the fixed length and known angles.
-
you could get all those lengths by dividing the triangle into 2 right triangles then using trig.
once the maths get involved to that degree, it'd probably be better to solve with grasshopper..
was just wondering if anyone can see some sort of geometric relationship in which things like mid snaps and mirroring and ??? can be used to solve.
? -
First speedy idea

Make your form a surface then
Seems you can use the "magenta" pinky inference ? (I don't remember the color)
Infinite solutions or maybe no solution for some dimensions?Imperial unities are chiness for me!

And problem seems more funny when your quadrangle is not plane and find the biggest or longer rectangle!
Seems some Fredo tools can help!

-
Yes the are an infinity of quadrangles!
If you make the inverse, Draw the rectangle on view top
You can draw any number of little triangle at the end of the rectangle
A anywhere on the left for have possibility to draw a triangleThen extend this little triangle and draw 2 big sides
Take a longer smaller than the end of rectangle so a constraint
Take a another longer smaller than the end of rectangle on the other side so a constraint again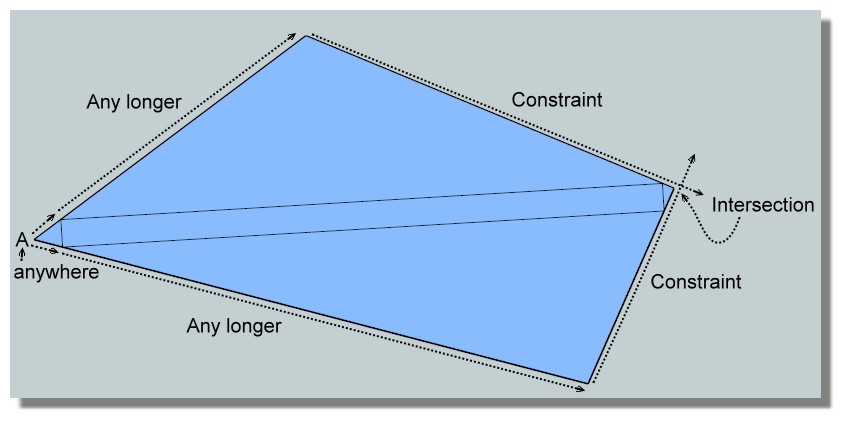
-
Yes Frenchy, in general. But I took Jeff's challenge to mean that all sides and angles of the quadrilateral were fixed and known. I think you can get from here to there using the cosine rule and some algebra, but banging my head against the possibility of a purely geometric, non-trig solution first.
-
@slbaumgartner said:
but banging my head against the possibility of a purely geometric, non-trig solution first.
don't bang tooo hard

fwiw, I saw this question at a rhino forum:
http://discourse.mcneel.com/t/geometry-riddle/14342at first, I thought it was going to be do-able via geometry but since then, a few very smart people have commented in the thread and/or posted solutions-- all of which seem iterative by nature (in some sense-- trial&error)
nobody has proven that a more simple (straight-forward) geometric approach isn't possible so that's why there's still a shred of hope but again-- don't bang your head too hard.
@frenchy-- yeah, doing it backwards (start with the 'board' and draw the 'room' around it) has infinite solutions.. (it also shows that an infinite number of gons can work. (4,5,6,etc) sided shapes can be drawn around the rectangle.
the question is the other way though.. start with a known shape and bisect it with a rectangle.(also-- units aren't important.. can be any unit and doesn't need to be imperial)
-
For shapes with an odd number of corners more info is necessary, as there is no innate definition of "opposite corner".
-
@slbaumgartner said:
For shapes with an odd number of corners more info is necessary, as there is no innate definition of "opposite corner".
right- once you've come up with a method, more info would be needed in the case of odd or multi numbered corners.. though i think the initial problem boils down to 'fit a rectangle between two angles".. the number of sides is irrelevant..

-
@jeff hammond said:
@slbaumgartner said:
For shapes with an odd number of corners more info is necessary, as there is no innate definition of "opposite corner".
right- once you've come up with a method, more info would be needed in the case of odd or multi numbered corners.. though i think the initial problem boils down to 'fit a rectangle between two angles".. the number of sides is irrelevant..
[attachment=0:qfxswsu7]<!-- ia0 -->Untitled.jpg<!-- ia0 -->[/attachment:qfxswsu7]
Right, but when you eliminate the full shape you have to provide more info to pin down the problem. You can move and rotate either corner without changing its angle!
-
ok
-
You need to know several things...
The distance between the two points where the angles are located [the line forming one diagonal of the quad']
You also need to know the four angles subtended to that line by each of the four lines forming the two angles.
From that you can do some calculations to give the range of x/y sizes for the potential rectangles that will touch all four lines [aka the sides of the quad'].
And i assume that no one quad' internal angle can be >180 deg ?
Does a rectangle that touches a side at the vertex itself 'in the limit', also 'count' ?
-
@tig said:
Does a rectangle that touches a side at the vertex itself 'count' ?
i suppose there are a few cases where a corner of the rectangle would coincide with a vertex of the quad (it would be the point at which if the angles were offset any further, that particular quad wouldn't have a solution at all.. not all quadrangles will be solvable)
for all intents and purposes, the .skp in the original post has an unsolved shape in which all the things which need to be known are known.. so, using that one as an example, can you find a solution for it?
-
@jeff hammond said:
has an unsolved shape in which all the things which need to be known are known.. so,
There could be hidden unknowns or maybe known unknowns, perhaps even unknown unknowns that we either do or don't, may or may not, have known about whether we know about not knowing about them or not.
-

-
@box said:
@jeff hammond said:
has an unsolved shape in which all the things which need to be known are known.. so,
There could be hidden unknowns or maybe known unknowns, perhaps even unknown unknowns that we either do or don't, may or may not, have known about whether we know about not knowing about them or not.
I don't know about that...
-
Who knows ?
...
Someone does...

-
From TIG's drawing
There are 6 constraints A1, A2, B1, B2, distance A-B and "thickness" of the inscribed rectangle
Thus we need, twice, a 7*7 matrix to solve each of the two corners (A-B). Who can define them?The solution must give the distance (radius of the tangent circle) between the axe of the inscribed rectangle and each point (A and B).
Advertisement







