[Info] Ambient Occlusion -> Simple Rays
-
just to thank you for such a plugin, it would be handy if progress.
-
This plugin is a great idea.
I would use the AO to overlay it on Vray renders.
Unfortunately I can't render the screen size 'as is' in Vray so I can't perfectly overlay them.
(I can't figure out how to use thomthom's ruby that is made to render the exact viewport using vray 1.00.74) -
I have added Bitmap.blur method to smooth out textures. I helps to save on calculation time, since now fairly good result can be obtained setting Rays to 5.
Here is an image showing the difference. Both shaded using Precision 10, Rays 10, but right one uses blur 3 times.
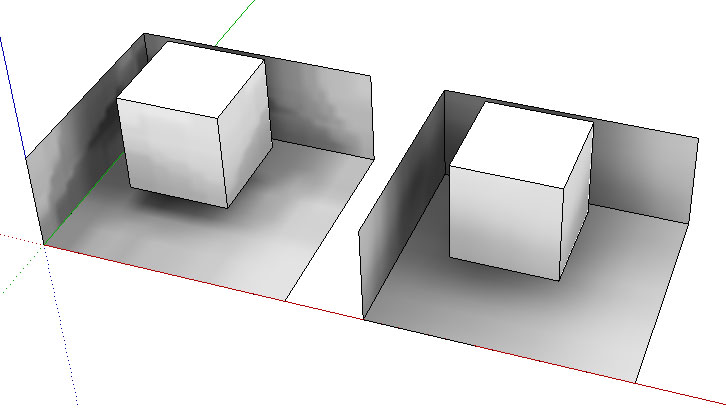
Does anyone have an idea how to replace model.raytest method with faster counterpart? Maybe there is a way to access OpenGL from Ruby?Kuba
ps. Just a tip. I turn on 'Use sun for shading' and set both 'Dark' and 'Light' to 100 just to remove Sketchup shading.
-
Kuba: nice work !
some suggestions:
- store directory and don't ask the user on each AO run for a directory
- make it Mac compatible - use Ruby functions instead of rindex for \
- to speed up things you need to profile the code and see what part takes most of the time
- add some progress info - Sketchup.set_status_text with % will do
- there is no way to access OpenGL from Ruby (except hijacking it but that will slow down SU)
-
TBD
Thank you for your suggestions. When the file is saved the script shouldn't ask for directory any more.
My biggest concern is model.raytest, it takes up to 90% of calculation time.
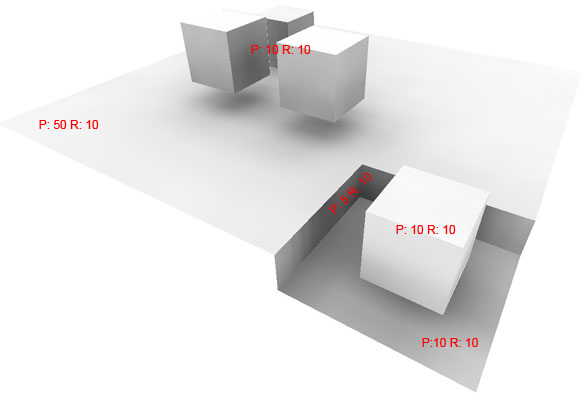
Can you tell me if you see any chance of speeding this plugin up? Is there a way to replace model.raytest? Is Ruby just to slow?Another example showing different settings for different sizes of faces rendered separately.
Kuba -
@qpik said:
My biggest concern is model.raytest, it takes up to 90% of calculation time. Is there a way to replace model.raytest?
unfortunately no

the only way is to take the 3d data and do the ray testing yourself, but definitely not in Ruby as it is too slow. -
@unknownuser said:
unfortunately no

the only way is to take the 3d data and do the ray testing yourself, but definitely not in Ruby as it is too slow.That is to say that this plugin has very little usability. It's just to slow.

TBD: It's probably a trivial question, but how do I extract file name from path on both Windows and Mac?
Anyway. I found that there is a strange thing with SketchUp resizing textures. Sometimes it's smother and sometimes it produces 'waves'. For example it gives nice result while using P:10, R:10 or P:25, R:10, but not with P:20, R:10 or P:50, R:10. (where P stands for Precision and R for Rays in AO settings)
Kuba
-
@qpik said:
It's probably a trivial question, but how do I extract file name from path on both Windows and Mac?
File.basename(Sketchup.active_model.path)and if you want just the name, without the .skp extension:
File.basename(Sketchup.active_model.path,".skp")@qpik said:
That is to say that this plugin has very little usability. It's just too slow
if you add overlaying on textures (adding support for .jpg/.png textures is enough) then it can be a free alternative to LightUp

-
Hello, I'm french this is a google translation.
This plugin is very promising, it interests me greatly, it will have on it manages colors, textures and shades diffuse projections in the future. But bravo, I am waiting for new version.
-
Thank you TBD. That saved me some time checking Ruby documentation
 I hope i fixed the bugs you pointed out in your first post. Let me know if it works on Mac.
I hope i fixed the bugs you pointed out in your first post. Let me know if it works on Mac.Also thanks to all for motivating posts. I cannot resist though to see dead end for this plugin.
Has anyone tried it on a normal model which has more than 10 faces? How long does it take to render?I still consider porting it to C++ (which I would have to learn
 ) but it seems pointless, as it's much easier I think to add texture baking to Podium or Kerkythea (if it's not there yet).
) but it seems pointless, as it's much easier I think to add texture baking to Podium or Kerkythea (if it's not there yet).Kuba
-
@qpik said:
Has anyone tried it on a normal model which has more than 10 faces? How long does it take to render?
tried on a selection of 47 faces (nothing complicated) - 8min 42sec on Quad Core 2.4ghz. a bit too slow

render in Podium of the complete model (106 faces) was 31 sec.@qpik said:
I still consider porting it to C++ (which I would have to learn
 ) but it seems pointless
) but it seems pointlessas you said that 90% is wasted in raytest I see no point in porting to another language except if you want to implement raytesting based on 3D data.
-
How about doing the raytest in Javascript via Webdialog?
Would that be faster than Ruby?Kuba
-
Hello there.
Since I need to calculate sun exposure time in my current project I've added this functionality to the plugin. Here you can see an example. Yellow corresponds to 10h exposure, blue is no exposure.
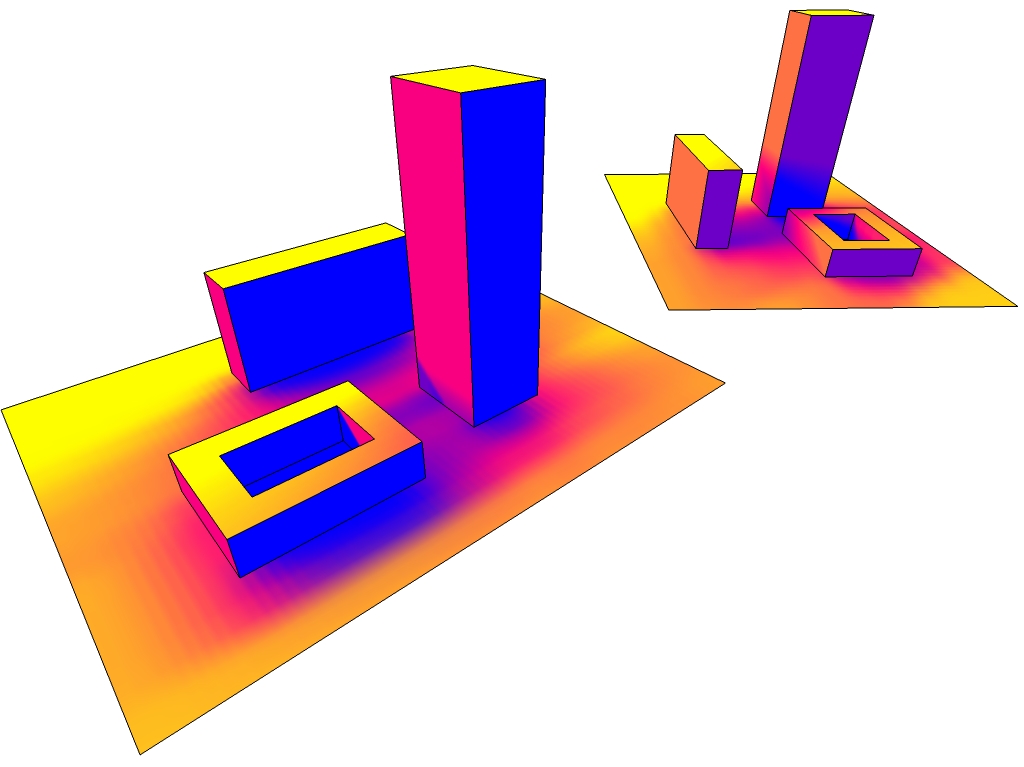
It is based on peculiar polish building code (which requires an apartment to have at least 3 hours of direct sunlight on vernal equinox between 7am and 5pm) making this version useful in Poland. It can be easily adjusted though to fit any location and sun position.ps. My previous question is still actual - Would doing the raytest in Javascript via Webdialog be faster than Ruby?
-
@qpik said:
How about doing the raytest in Javascript via Webdialog?
Would that be faster than Ruby?To get this to happen at all in Ruby is heroic. I'm impressed.
Neither Ruby nor JavaScript is a compiled language. C++ may be an order of magnitude better.
-
Does anyone know if there is a way of creating a faster replacement for
model.raytestmethod?
I've found a Ruby PNG library. That's a step towards layering textures in Sketchup (using PNG alpha).
Kuba
ps. Would anybody like to cooperate on this plugin?
-
This is really amazing. I mean, if you could do the raytesting separately with a faster language, it'd be really useful.
-
The
.raytestmethod is running in SU's C. Not calculated using Ruby. Ruby just calls the C method. -
Does that mean that
model.raytestalgorithm is inherently slow?
So I would need to write my own in C. -
What I meant was that the
.raytestis probably written in C already. -
Yeah, to make it faster wouldn't you need to export the geometry so an external routine could both loop and perform the raytest?
Advertisement







