Sine Law?
-
I need help in writing a Ruby equivalent sine law......TIA!
example: Calculate angle B
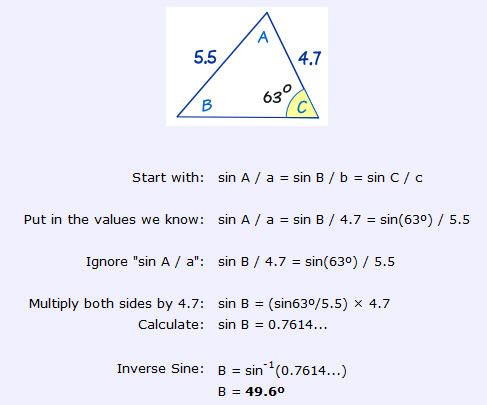
-
Let's call angles
aa,abetc, and lengthsda,dbetc...
Notes: if the angles you have are in 'degrees' then pass it in 'radians' to the Math function using theaa.degreesmethod, otherwise if they are already in radians use their float value...
To turn a 'radian' result into 'degrees' use the.radiansmethod...Math.sin(aa) / da = Math.sin(ab) / db = Math.sin(ac) / dcFirst pick the pair of == which contain three knowns and the one unknown value you want - '
ab'...Math.sin(**ab**) / db = Math.sin(ac) / dcChange the subject of the formula [i.e. multiply both sides by '
db']...Math.sin(ab) = db * Math.sin(ac) / dcor to get '
ab' in radians use '.asin'...ab = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac) / dc)Then to see '
ab' in degrees:ab = ab.radiansdb=4.7; dc=5.5; ac=63.degrees; ad = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac) / dc).radians
49.5882674686285To round the answer to 1 d.p. use:
ad1 = sprintf("%.1f", ad)
49.6
The higher the.Nfthe more d.p.s
Note that in the above example '[ruby:anl6c1ws]ad1[/ruby:anl6c1ws]' is a string - to get a float use:
[ruby:anl6c1ws]ad1=ad1.to_f[/ruby:anl6c1ws]

-
2 added issues which I have not been able to find diagrammatically illustrated in the Ruby math code:
(I use globals only to verify the values in the console after the ruby has run)- How to subtract angles?
# Angle aaa = 180 degrees - angle aa $aaa=180-$aa # 119.026476570893 # Angle ccc = 90 degrees - (Angle cc +Angle bb) $ccc=90-($cc+$bb) # 27.2834559031268- How to append an angle value to angle value.degrees?
incorrect:
# Sine Law; does not give the right answer $da=Math.sin(($aaa)*$dc/Math.sin($ccc)).radians # 56.3706471942142correct answer after I manually added .degrees:
# Sine Law; with the correct answer $da=Math.sin(119.026476570893.degrees)*dc/Math.sin(27.2834559031268.degrees) # 135.21551555127 !OKTan angle to degrees?
# Angle aa $aa=Math.atan(($raheight-$radepth)/($length/6)).radians # 60.9735234291066 !OK but .degress is missingFind length $da
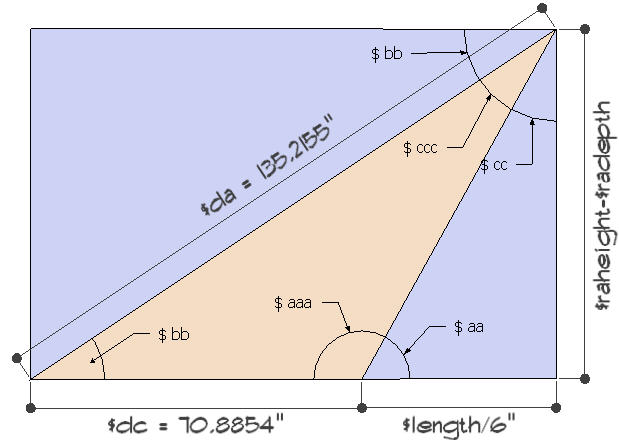
-
Yes... you must always work in radians.
Most programming languages use them for angles.
SketchUp has the useful numeric additions, so 60.degrees converts an angle of 60 degrees into radians for you, and conversely 1.0471975511966.radians converts that value to ~60.0 degrees... -
I see some gaps exist in my previous query:

The Ruby Math Module has the job of evaluating math expressions. Its up to the programmer to provide the proper units. In fact regardless of the units I provide, the resulting evaluation only provides the numeric value, the units are never displayed in the ruby console.
In this particular case, I need the ruby code to include the value and the units: , which is .degrees in this example.
But because the global contains only the numeric value, the global substituted into the sine law, provides the wrong answer.I order for the Sine Law to provide the correct answer, the global substitution needs both the numeric and unit value:
I would like the ruby code to make the correct substitution. Not manually as I illustrated.
-
And the problem is

There is no problem... just decide on what units are used and then use .degrees or radians if the input is not in 'sensible values'...
I fail to see what issue you have here

-
Ok!...... one more time, lets see if can get my question across

Lets take a portion of your nicely illustrated example of the Sine Law.
db=4.7; dc=5.5; ac=63.degrees; ad = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac) / dc).radians
49.5882674686285ad = 49.5882674686285 but more importantly if I were to use the value ad and substitute its into lets say another sine formula I would NOT get the correct answer. because the .degress is missing.
So my question is How do I get ruby to append .degrees to the value ac = 49.5882674686285
-
The method
.degreesturns an angle that is in degrees into radians.
The method.radiansturns an angle that is in radians into degrees.
So...db=4.7; dc=5.5; ac=63.degrees; ad = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac) / dc).radians 49.5882674686285
Then later...ad.degrees 0.865478537687162
BUT of course if you has missed off the final.radians'ad' would already be in radians... and therefore to see it in degrees you'd need to usead.radianslater...
I suggest you get input in degrees AND also return amgle angle answers in degrees too: only changing the angles to be radians when you use Math functions that are needing them...
Soac=**63.0**and then in the equationad = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac**.degrees**) / dc).radians
Now 'ad' is in degrees again, so when you Math equation processes it usesad.degreesYou are over thinking this... it's pretty straightforward.
Don't mix up degrees and radians as you'll get confused...
Keep the 'degrees' for the 'human-side- and just use.degreesto convert to 'radians' for Ruby's 'Math-side'...
-
@tig said:
So
ac=**63.0**and then in the equationad = Math.asin(db * Math.sin(ac**.degrees**) / dc).radians
Now 'ad' is in degrees again, so when you Math equation processes it usesad.degreesI was not confused between degrees and radians. Its the same way angles are treated in many languages, I'm quite familiar having written AutoLisp routines years ago, which also uses degrees and radians. Its more about me learning how to write the same code in Ruby
.........I finally see in your example how .degrees gets added, its really simple once I saw your example.
Advertisement







