3D Truss Models
-
I'm now at the stage where I am beginning to work through my algorithms for the actual framing of the roof (ie. rafters, ridges, hips and valleys). I begin by breaking down the edges of the roof so that I can determine which are hips, valleys, rakes, flying hips etc... I also want to actually label each as such so when it comes time to dump all of this into the estimating module there is some order to it.
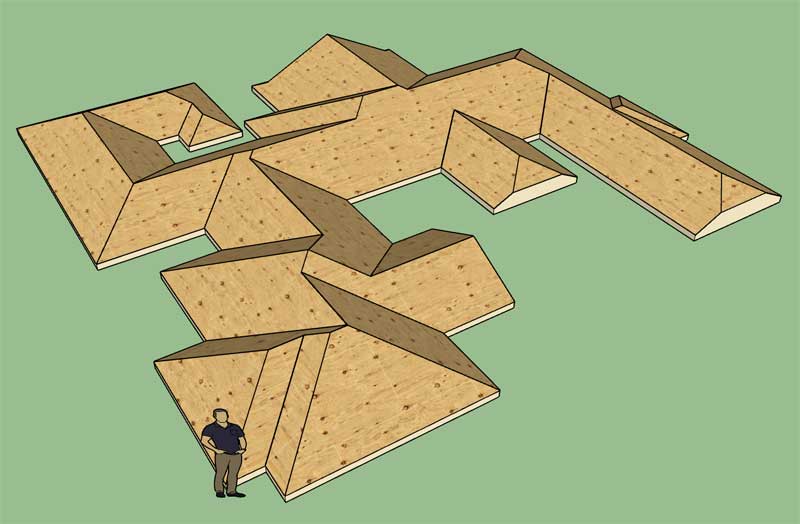
If you look closely at a roof primitive and the edges that constitute that primitive, immediately a number of things jump out at you:
1.) All of the horizontal edges that are at the same Z height as the top fascia line are roof perimeter edges or "fascia edges". We do have to make an exception for the half hip though, since its fascia edge will be elevated above the eave height.
2.) All of the edges with vertices below the fascia Z height are irrelevant and we won't be needing those.
3.) If we look at all the edges coming off of the perimeter vertices (we can find those easily enough by comparing against our perimeter points array) it is apparent that the inside angle between two fascia edges will determine whether the edge is a valley or a hip. If the angle is less than 180 deg. then it is a hip. if the angle is greater than 180 deg. it is a valley. If the edges belong to a gable or half hip roof plane then they will be rake edges, rather than hips or valleys.
4.) Next we grab all of the remaining edges where the height of the start and end vertices are equal. These will form ridges. An exception must be made for dutch gable and the half hip. So it is best that we eliminate those edges first.
5.) Fortunately, there are no such thing as flying valleys, only flying hips. By process of elimination the remaining edges will all be flying hips. Flying hips are interesting because they always begin where a valley and ridge intersect and they end either intersecting another hip/flying hip at a ridge or at a peak with possibly multiple hips coming together at a point.
We basically dump each edge in the primitive into a hash so we have ourselves a quick lookup table for each edge that we can access it for future operations (ie. cutting rafters).
When the roof corner angles are all orthogonal (90 deg. or 270 deg.) the algorithm for the rafter framing should be fairly simple. However when you throw in non-orthogonal angles (ie. octagon roofs) things become more complicated and there needs to be some logic to deal with these scenarios specifically.
Another reason that I need to classify the edges is that the width of the valleys, hips and ridges may not be equal, which will impact the trimming of the rafters as they intersect these members.
And that is all the magic there is to it. I think the key breakthrough I had back in May (when I figured out my straight skeleton algorithm) was that I realized that once I somehow generated the roof primitive the rest would easily fall out. Previously, I was trying to mathematically calculate all of these vertices and edges, which turned out to be incredibly difficult and ultimately a dead end.
I now have a coherent plan of attack.
-
I've also been giving some thought to gutters. If there are no half hip or gable conditions the gutter will wrap completely around the roof.
Otherwise the gutter will be broken into one or more sections.
Downspouts are more of an issue. With a complex roof the positioning of downspouts needs to be more customizable. I would like to implement a system where the user can select standard locations to position downspouts along a gutter run. For instance at either end or at the middle, this should provide enough flexibility for most situations.
-
@medeek said:
I've also been giving some thought to gutters. If there are no half hip or gable conditions the gutter will wrap completely around the roof.
Otherwise the gutter will be broken into one or more sections.
Downspouts are more of an issue. With a complex roof the positioning of downspouts needs to be more customizable. I would like to implement a system where the user can select standard locations to position downspouts along a gutter run. For instance at either end or at the middle, this should provide enough flexibility for most situations.
Are you going to provide an interface where parameters will be set, to be adhered to, for the sizing of gutters and downpipes (thus relating to number of) based on the plan area (not actual, but measured perp from above) of the roof served?
-
Tutorial 16 - Introduction to Complex Roofs (19:42 min.)
I did forget to mention the "Edit Outline" function which can be initiated by right clicking on the roof assembly. However, if you have a number of customized roof planes the results may become unpredictable, especially if the the outline is dramatically changed. The feature will need some further refinement.
-
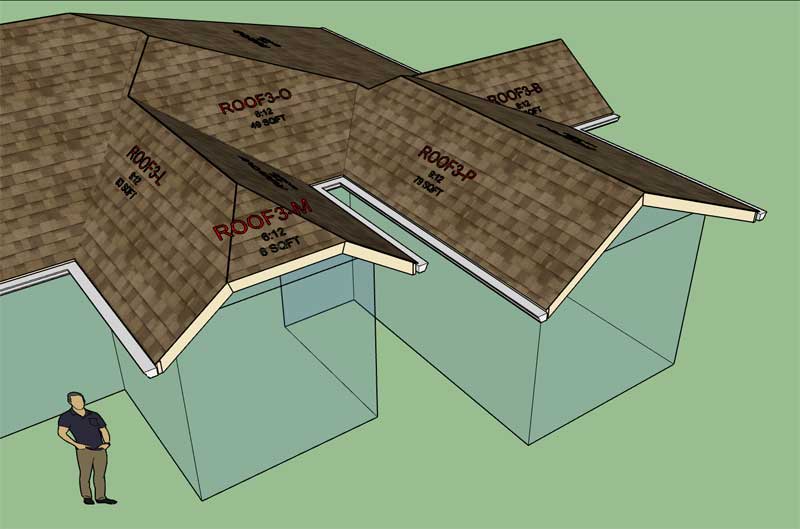
First look at a gutter fully wrapping a complex (hip) roof:
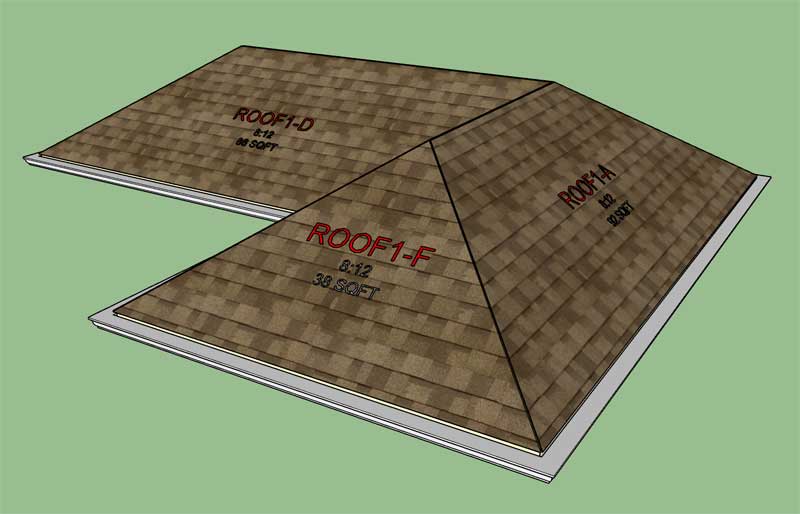

Note the 3/4" offset from the sub-fascia since I have soffit and fascia enabled. The 3/4" thick fascia is not drawn yet, hence the gap.
I've also set my vertical offset to 1" for the gutter.
-
Version 2.5.6 - 10.11.2019
- Added gutters for complex roofs.
View model here:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
On this particular model I've employed a vertical offset of 1" and a gutter extension of 1.5" with a K5 style gutter, other gutter styles available.
I have not enabled downspouts yet as I need to come up with a better system for handling these. I think I have a new system figured out but I need to work on the details before I'm ready to implement it.
-
The problem with complex roofs is that I am only scratching the surface right now. There are quite a few permutations that are possible that are quite common with many residential designs that I still cannot handle with the current complex roof module.
Consider this relatively simple example:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
With this case the fascia is at two levels. At the back corner on roof plane A you have what I call a 3/4 Hip (kind of hybrid between a half hip and a hip, one side is a hip and the other is technically a half hip). This causes the fascia line to rise by 24".
Where roof plane E meets roof plane D, you have one roof plane dying into the other and creating a "Flying Valley" and the other roof plane terminates at the wall below (a partial gable end?).
I guess I was wrong there are "flying valleys" after all.
The problem with trying to construct this particular example with my proposed secondary roof module is that its a little more complicated than that. Rather than two separate roof assemblies the roofs are technically merged. Also the 3/4 Hip configuration kind of requires that the roof assemblies are one construct.
This example really has me scratching my head right now.
What does jump out at me is that when you are dealing with an inside corner (angle between walls is greater than 180 deg.) the roof planes die into each other creating a partial gable and a flying or hanging valley.
When you have an outside corner (angle between the walls is less than 180 deg.) you then end up with a 3/4 hip. Two additional solutions might be a gable or half hip with unequal legs. If you were to keep making the setback of the half hip larger eventually it would degenerate into the 3/4 hip where one leg is now a hip roof.
-
My original restrictions on the placement of gable ends are too tight. In order to created roofs where you may have a gable on a gable we need to relax things a bit or at least change up the conditionals:
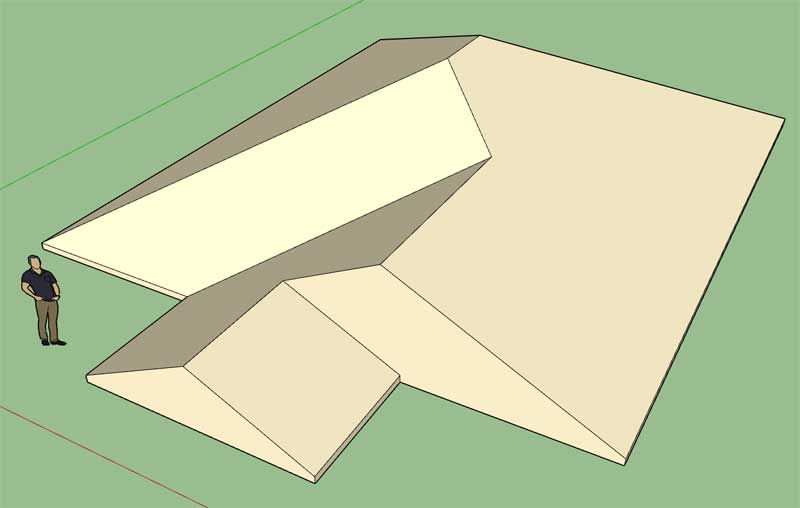
This further complicates each building element or at least opens up possibilities which did not exist before so I will need to add additional logic for sheathing, cladding, sub-fascia and gutters.
Who said complex roofs were going to be easy.
-
Another variation of the gable roof study:
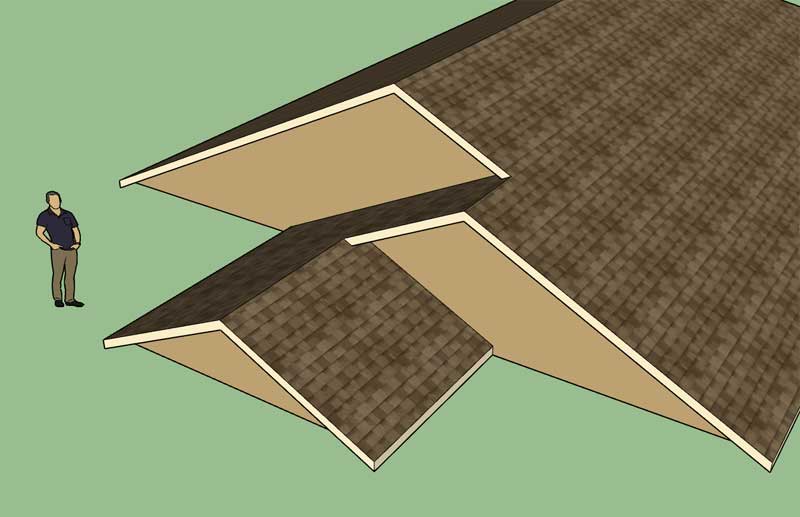
Gables ad infinitum...
The one thing that jumps out here is that gable roof planes cannot be adjacent to each other (or other variants like dutch gable or half hip configurations), gable roof planes are separated by hip planes. Additionally, I will limit the gable option to orthogonal roof planes only (corners must be 90 or 270 degrees).
There is always on more thing to add, at some point I hope to have conquered this beast.
-
When you raise the fascia line along a segment of the roof inevitably it must return to same level since a roof is a closed loop. See model here:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
I think I can make this work but I'm going to have to drastically change my algorithms to allow for unequal fascia/gutter lines.
The other interesting thing with all of this is that the fascia line could step up and down multiple times around a roof.
Another observation is that only hip roof planes technically step up or down, gable roof planes/edges are controlled by the adjacent hips.
-
A couple of interesting gable roofs:
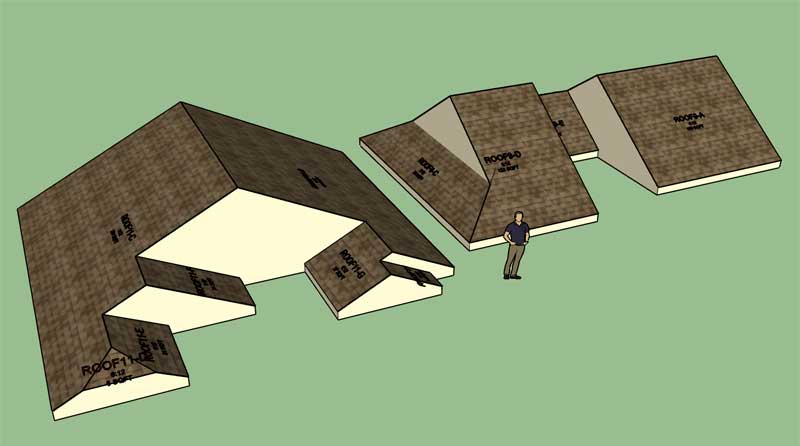
Looks like I have the roof primitive working for "interior" gables. Now I just need to sort out the details for sheathing, cladding, sub-fascia and gutters. An interior gable is defined as a gable roof plane with one or more corner angles of 270 degrees (orthogonal inside corner), hence an interior gable.
For now I'm not going to allow interior dutch gables or half hips. As long as the angles, at both corners, are 90 degrees then you will be able to place a dutch gable or half hip on that roof plane. However, the gable is a little more flexible and will allow some interesting configurations, as shown.
-
Notice how the sheathing is now projecting underneath the gable overhangs:
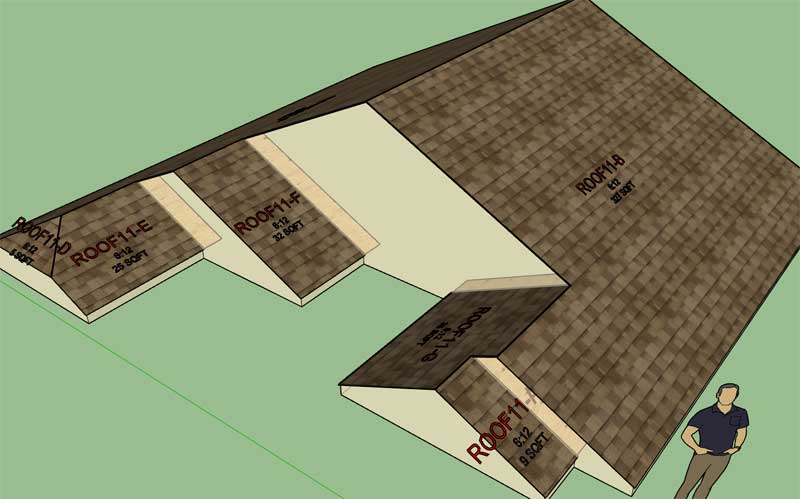
Now I just need to get the cladding to behave similarly and then a few adjustments to the sub-fascia and gutters.
-
First look at cladding correctly displaying for interior gables:
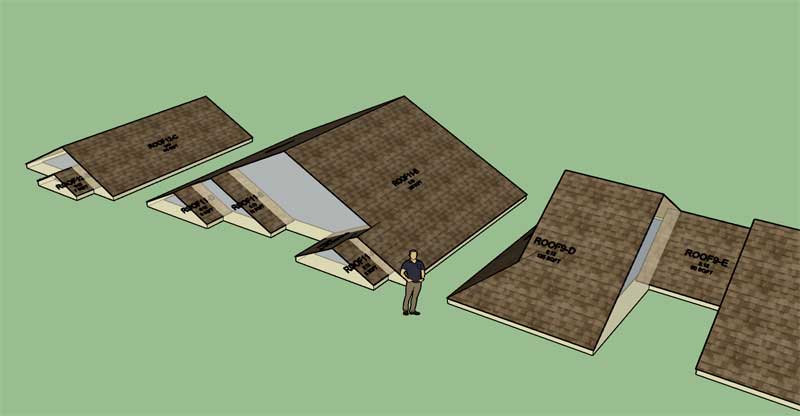

The sub-fascia for interior gables is interesting because in most cases one or both side will die into another roof plane, however this is not always the case as can be seen in the example to the far left. Logic to include all of these possibilities now must be constructed.
Unlike the much simpler exterior gable the position of the peak of the interior gable roof has no direct relation to the perimeter points that define this gable's edge. Due to this inconvenience I cannot (easily) mathematically calculate the sub-fascia, I must use the roof primitive geometry to derive the correct points and position, again more emergent behavior. In short, the roof primitive is smarter than I am.
-
First look at sub-fascia for interior gables:
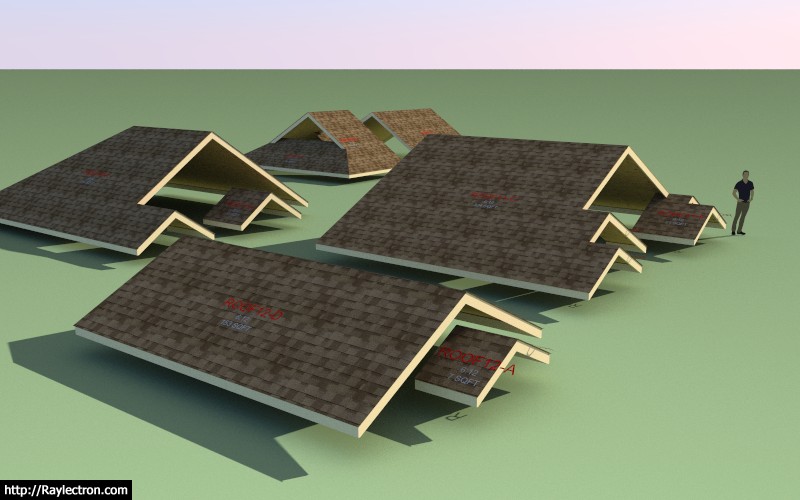
Bit of a struggle to consider all of the possible permutations for this type of roof but I think I have finally arrived at a robust solution.
I just need to consider gutters and then we can proceed with the actual framing of the roofs.
I've also heavily modified my error checking code for the roof primitive to make the overall performance more robust. With the addition of interior gables there is more probability that the designer can create roof design that does not have valid geometry. Further testing will be required to try and eliminate these scenarios or further augment the areas that are having trouble with these situations.
-
Version 2.5.7 - 10.14.2019
- Allowed the option for interior gables within complex roofs.
- Fixed a bug in the gutter module for complex roofs.
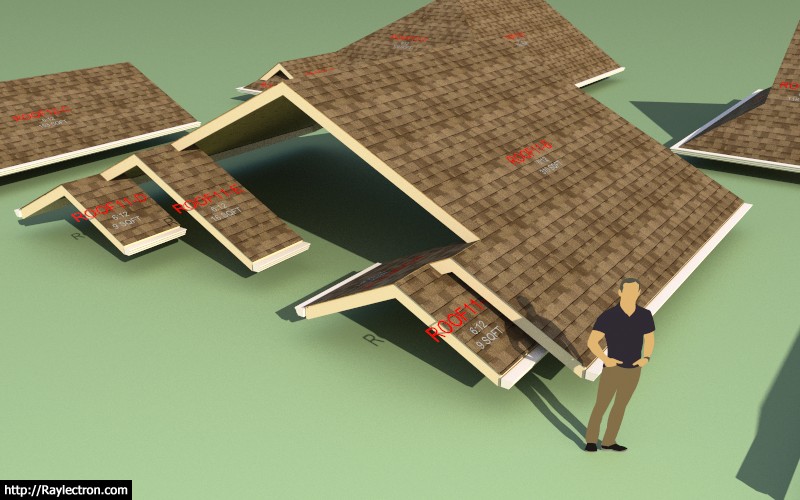
I need to do some traveling in the next few days but I just wanted to get the update out the door before taking a break from the code.
View model here:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
-
As I'm taking a break from the code before my trip it dons on me that the soffit & fascia, primarily the fascia is probably more important than the actual roof framing right now. If I have that feature enabled it will allow the designer to complete his or her elevations. Whereas the framing is a critical future feature but does not really come into play for the actual construction documents.
With that in mind, I think my next big push will be to complete the soffit & fascia, then I will begin the framing algorithms. The good news is that the fascia algorithms will be very similar to the sub-fascia so most of my work there is already done.
Also speaking to a number of plugin clients earlier today it took me back at how many of them actually use AutoCad for their construction documents, and just import parallel projections from SketchUp as a DXF/DWG. Even though the resulting mess of "dumb lines" in your AutoCad drawing is not optimal I suppose it is still quicker and easier to do this rather than to try and actually draw a complex roof elevation from scratch.
-
More gables:
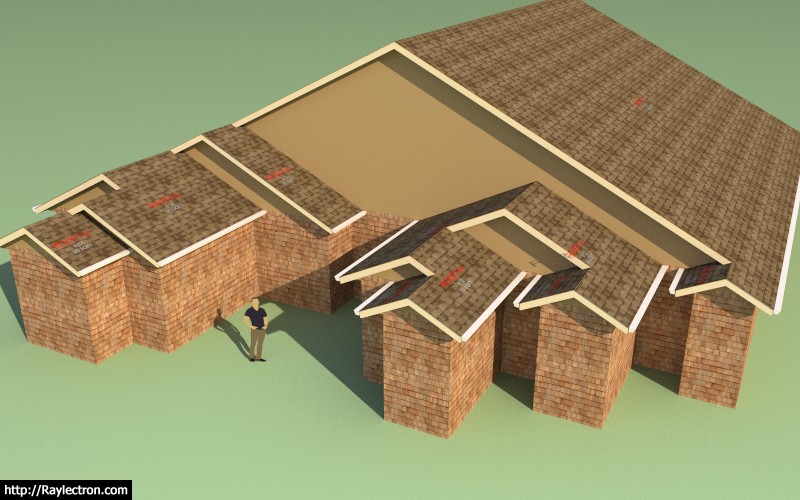
View model here:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
-
I will be out for 2 - 3 days however you can probably reach me by phone if it is an emergency, however I won't have any computer in front of me so it may be hard to do any significant support or troubleshooting.
I had an interesting conversation with a client today and he wondered if I disliked engineering, and that is why I am now developing plugins. I do not dislike engineering, in fact I really would like to get back into it but I would like to get back into it with SketchUp and my plugins leading the charge.
The one problem I have with the way residential engineering is done (or at least the way I was doing it), is the lack of automation. Yes, there are plenty of tools out there (spreadsheets, Forte etc...) that help with the calculations, however I want something even more streamlined. I want a program that already takes a 3D model of a structure and then is somehow smart enough to propagate the loads throughout that structure and run all the numbers automatically. This is the way engineering should be done in the 21st century, we have the computers, and yes we have the technology, we just need to leverage it so that we can stop wasting our time on tedious chores.
To be honest, most of residential engineering is quite mundane. There is some engineering judgement that comes into play in certain situations however for the most part it is merely taking some inputs and running them through a number of AWC and ASCE equations and giving the result a GO or NO-GO. This is exactly what computers were built for.
This is my vision for the engineering module and what it should be able to do:
I should be able to enter the site criteria for a project and then with the push of a single button crunch all of the engineering calcs for that model. The items that fail will be flagged. I modify those items accordingly (upgrade a header to a larger size), and then run the numbers again, until everything passes. I then click the generate report, a PDF is generated. I review it one last time, checking for errors and making sure all the inputs and outputs look reasonable and consistent, and then print out a paper copy, and stamp and sign it.
I've decided my time is much better spent developing a proper solution like this rather than continuing my practice of manually crunching numbers for local residential clients. Undoubtedly, I would make more money working on local engineering projects than I would make working on just these plugins (full time). In fact, I even turned down an employment opportunity last year for a really nice, six figure income so that I could specifically pursue the Wall plugin full time.
Currently I'm probably only making only about half of what I could make working strictly as a conventional engineer or corporate drone, but with me it has never been about the money. One has to look at the big picture with these things. I love what I do, I have full ownership, and I am able to help hundreds, maybe thousands of architects, engineers and designers rather than just a handful of local clients. Every day I wake up I get to decide what needs to done, I control the direction I take, even though my customers do guide me. I am also able to leverage both my love for programming and my love of engineering. I didn't choose this path, it chose me.
-
First look at fascia with complex roofs:
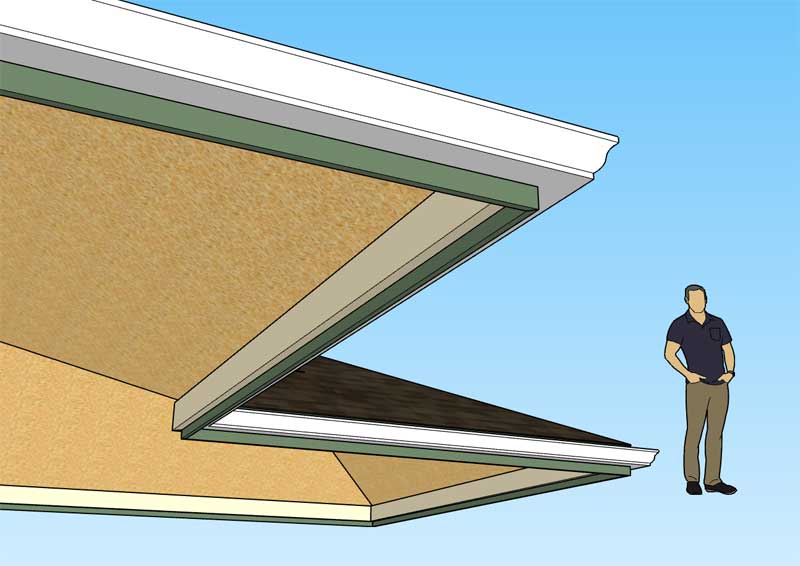

View model here:
3D Warehouse
3D Warehouse is a website of searchable, pre-made 3D models that works seamlessly with SketchUp.
(3dwarehouse.sketchup.com)
Now I just need to look at the various permutations for various roof end configurations (ie. gable, half hip, dutch gable).
With gable and half hip configurations we also have Boxed, Angled or Gable style configurations.
-
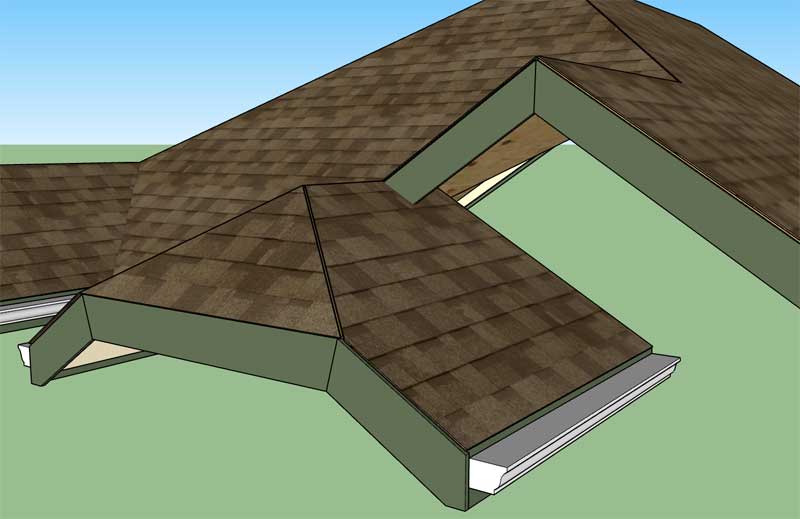
First look at a half hip fascia and rake with a boxed soffit:
Advertisement








