Alpha transparency in back face
-
I've made a simple model to help understanding.
Open it and you'll see a single face, but its actually rhomboid with the "sides" facing toward the camera direction.
You can't do a worldspace test to determine visibility in a non-orthonal projected space.
EDIT: well thats not entirely true, but you need more than camera.direction.
-
maybe I did not understand, but if I could see the faces covered and their normals (which geometrically can do), normals vectors should be away and not to my point of view. Which would mean that I would be looking at the back of the faces .... but maybe I did not understand what you mean, later will study better, thanks!
-
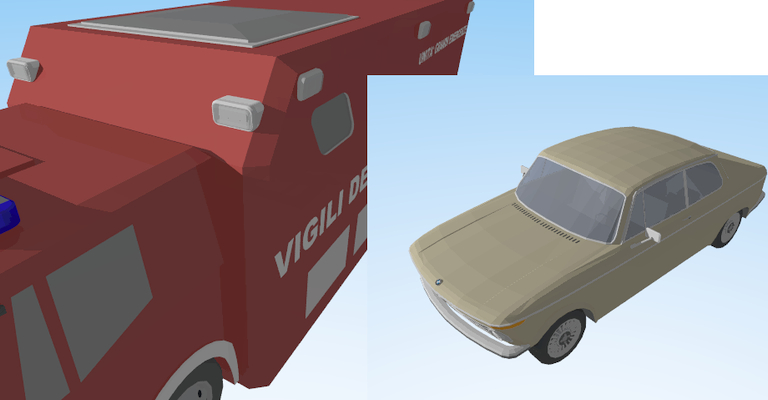
The simple to apply an OR between the sides seems to work well. Note that the windows of the truck were opaque even on SU, but now the lights are transparent, the same of SU.
I have to test it on various models, because my old version of the plugin to import in PovRay exchanged opacity values and I have to fix the little problem. SU uses the opacity value, and instead using PovRay I usually write the transparency. So I have to make complementary to 1. I did not realize at that time because with 50% of transparency (more or less) the results seem to be equal .... Then the next day I will update the plugin .... thanks

-
My conclusions.
Generally the principle of OR between the two sides of a face works for transparency, because it is always quite reasonable that the apparent transparency is equal between the views from inside OR outside.
Instead, the problem is more serious for the color.
SU does not differentiate inside and ouside of each face and objects does not apply evenly the principle of the right hand.
Faces and back faces are not always oriented toward the outside the first and the second inward.
For this reason, when exporting is important to check the normal to choose the right color (if the colors are two) for export to the face.
The methods exist, it is only a matter of working on it, even if it is not simple.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Back-face_culling
In the image, the example, part of the truck (sketchup object found in the web) with the door designed with the order of the clock and also with the reverse order. (image of MeshLab after I imported some faces of the truck converted in STL format)
sorry for the bad English, I hope it is at least understandable

-
So you have finally realized that sloppy modeling leads to back-face issues.

That is why I developed http://sketchucation.com/pluginstore?pln=FixReversedFaceMaterials
View the model in Monochrome mode, so that you can see visible 'back-faces' in a distinctive color set in the Style.
There are several tools to flip [reverse] the face so its 'back' is then facing the correct way.
BUT these faces will then take their material with them, perhaps leaving a default [or other unexpected material] front face visible.
My tool reverses any [selected] face with a material on its 'back', AND then reuses its back-material onto its front, keeping any UV-mapping, and it then defaults the back material of the face too.
There are other tools which reverse faces, and swap the materials between the face's sides too [thomthom has one...] -
really, more than I have to figure out how to draw, I have the opposite problem, I certainly do not model these objects so sloppy, (and redundant, but that's another matter) because I'm used to working on a real CAD for a lifetime . It took me a long time to realize that SU uses safely the back face as a front face, pulling on the front his color back ..... so I will have to develop a filter that normalize the entire model. My problem is not learning how to draw, but how import those models that do not have a decent description of the points .... thanks

I will check your code !
tar=cam.target
vec=eye.vector_to(tar)
if vec.angle_between(face.normal)>90.degrees ..... -
Tig, I checked, but AdamB is right ...
@adamb said:
@tig said:
In code you can ensure a face's normal is towards the camera [get angles between the view direction and the face.normal], if >180 you are looking at the front !
TIG, strictly this is only true for a parallel projection. Its broadly correct for perspective projection, but not for all cases.
The search for the "internal" and "external" of the object, this is the only way to evaluate the order of the vertices of the faces.
Instead, this code seems to be a solution.
It is a raw code ... it investigates only the skin of a compact object, devoid of undercuts ... but I will write the recursive routine. the ray must to come and to go in the solid, each IN must find his OUT in the space, and to end this way in the open space, switching the on - off ... otherwise the beam was started by a face looking at the inside of the object, and the normal of that face watch inside (what I have to correct) ...if face.material==nil #and face.back_material!=nil model = Sketchup.active_model vertx=mesh.polygon_at 1 ray = [mesh.point_at(1), face.normal] item = model.raytest(ray, false) if item.to_s.length!=0 then # UI.messagebox(item.to_s.length.to_s) face.reverse! # face.material=face.back_material # else # UI.messagebox("ok") end endPS: at this moment in the code the point is one random of the face vertexes, it would be better to define an interior point on the plane of the face, which is not disturbed by any adjacent faces at 90 degrees that can confuse
Advertisement







